The Art and Science of Sheet Glass Manufacturing
Sheet glass manufacturing is a remarkable blend of art and science that plays a pivotal role in various industries. From architecture to automobiles, sheet glass serves as an essential material that offers clarity and strength. The process of creating this versatile material involves several intricate steps and advanced technologies.
The journey of sheet glass begins with the selection of raw materials. The primary ingredients used in manufacturing sheet glass include silica sand, soda ash, and limestone. Silica sand provides the essential silica component, which is the primary building block of glass. Soda ash acts as a flux, lowering the melting point of silica, while limestone helps to stabilize the glass structure. The right proportions of these materials are crucial to ensure the desired quality and properties of the final product.
The Art and Science of Sheet Glass Manufacturing
After reaching a uniform state, the molten glass is shaped into sheets through various processes. One of the most common methods is the float glass process, which involves pouring the molten glass onto a pool of molten tin. This method allows the glass to spread evenly, creating a flat and smooth surface. The use of tin helps in achieving a perfect finish since it prevents the glass from sticking. As the glass cools, it solidifies, forming a continuous sheet.
sheet glass manufacturing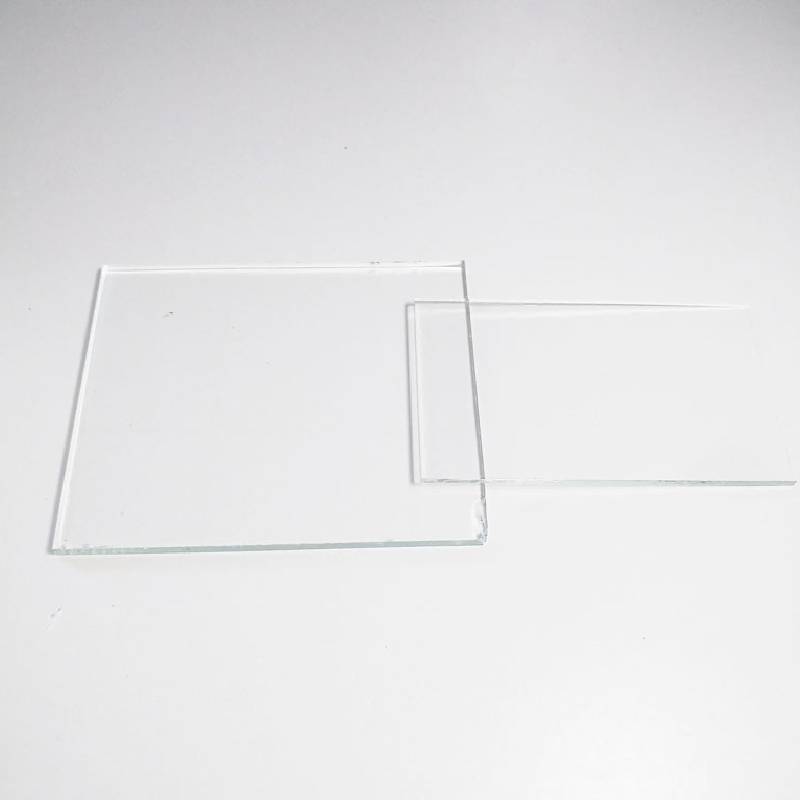
The formed sheet glass is then annealed in a controlled environment to relieve internal stresses. This step is crucial as it enhances the durability and strength of the glass. Annealing involves slowly cooling the glass to room temperature in a process known as an annealing lehr. This controlled cooling prevents the development of cracks and imperfections, ensuring that the glass meets the stringent quality standards required for various applications.
After the annealing process, the glass sheets are cut to the desired dimensions, polished, and inspected for quality. Various tests are conducted to ensure the glass meets safety standards and performance criteria, including impact resistance, optical clarity, and thermal stability. Once approved, the sheet glass is packaged carefully to prevent damage during transportation.
The advancements in technology have also led to the development of specialized sheet glass products, such as low-emissivity (Low-E) glass and laminated glass. Low-E glass is designed to reflect heat while allowing natural light to pass through, enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass with an interlayer that provides additional safety and sound insulation.
In conclusion, sheet glass manufacturing is a complex yet fascinating process that combines raw materials, high temperatures, advanced techniques, and rigorous quality control. The result is a versatile product that finds applications in numerous sectors, significantly contributing to both functional and aesthetic aspects of modern design. As technology continues to evolve, the future of sheet glass manufacturing holds much promise for further innovation and sustainability.
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu 

