Understanding Standard Float Glass An Essential Material in Modern Construction
Standard float glass is a fundamental material widely utilized in various architectural and industrial applications. Known for its clarity, strength, and versatility, float glass has become a staple in windows, doors, and numerous other installations. This article explores the properties, manufacturing process, and applications of standard float glass, highlighting its significance in contemporary materials science and construction.
What is Float Glass?
Float glass is a flat glass product manufactured through the float process, which involves melting silica sand, soda ash, and limestone at high temperatures to form molten glass. This molten glass is then floated on a bath of molten tin, resulting in a smooth and uniform thickness. The floating method allows for the creation of large, flawless sheets of glass, free from imperfections that often plague other glass types. Once cooled, the glass is cut into sheets of various dimensions, which can then be further processed for specific applications.
Properties of Standard Float Glass
One of the defining characteristics of standard float glass is its optical clarity. It has a high light transmission rate, making it an ideal choice for applications requiring transparency, such as windows and display cases. Additionally, float glass has excellent durability, offering resistance to weathering, scratches, and chemical exposure. Its smooth surface makes it easy to clean and maintain, contributing to its long-lasting performance.
In terms of thermal properties, float glass has a moderate level of thermal conductivity and resistance, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor settings. However, it is important to note that standard float glass is not inherently energy-efficient. The development of low-emissivity (low-E) coatings has enhanced its energy performance, allowing for better insulation and reduced energy costs in modern buildings.
standard float glass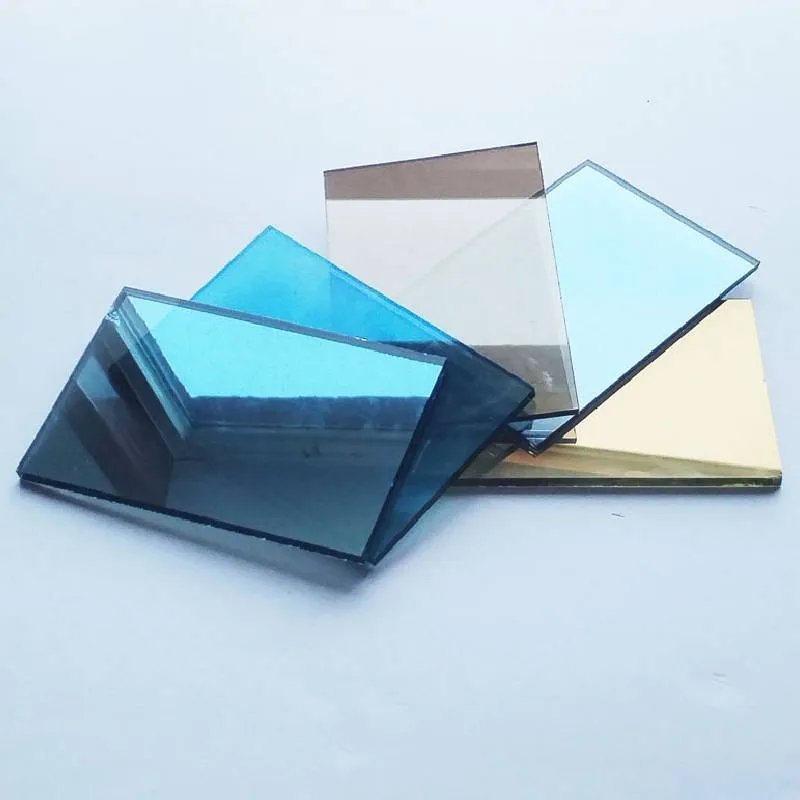
Applications of Standard Float Glass
The versatility of standard float glass extends to various sectors, including residential, commercial, and industrial applications. In the architectural realm, it is commonly used in facades, curtain walls, skylights, and partitioning. Its aesthetic appeal and ability to create bright, open spaces make it a favorite choice among architects and designers.
In addition to construction, float glass finds applications in automotive manufacturing, where it is used for windows and windshields that require high clarity and strength. The optical properties of float glass are also harnessed in the production of mirrors and glass furniture, contributing to the modern design aesthetic.
Furthermore, float glass is increasingly being integrated into smart technologies as innovations in glazing surfaces arise. This includes solar control glass that regulates heat gain and loss, as well as glass that can be transformed into interactive displays, showcasing the ongoing evolution of this timeless material.
Conclusion
In summary, standard float glass stands as a quintessential element in the world of construction and design. Its unique combination of clarity, durability, and versatility ensures its continued relevance in modern applications. As technology advances and the demand for innovative building materials increases, float glass will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of architecture and beyond.
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu 

