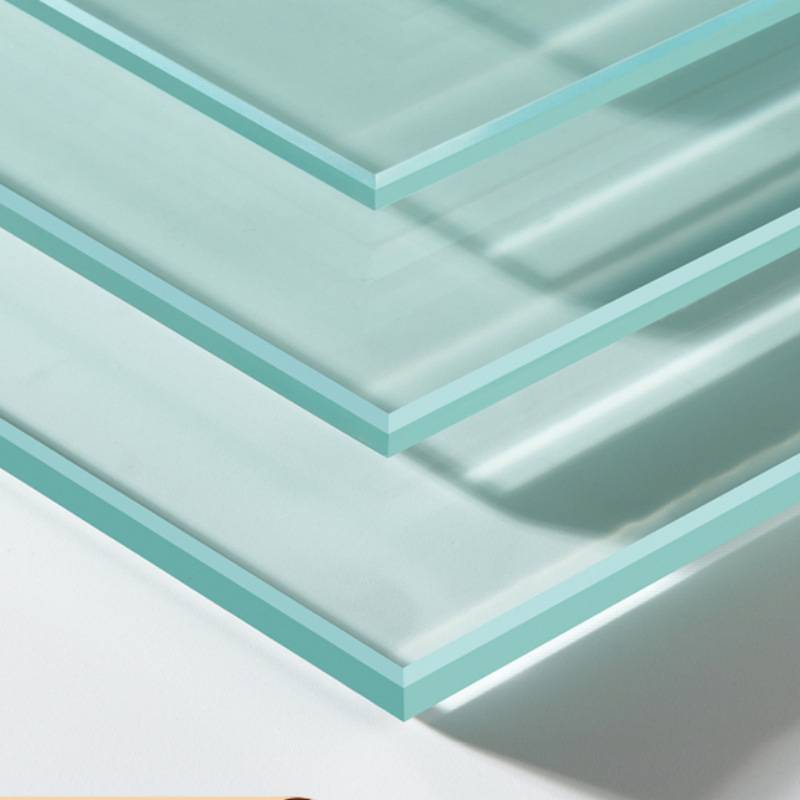
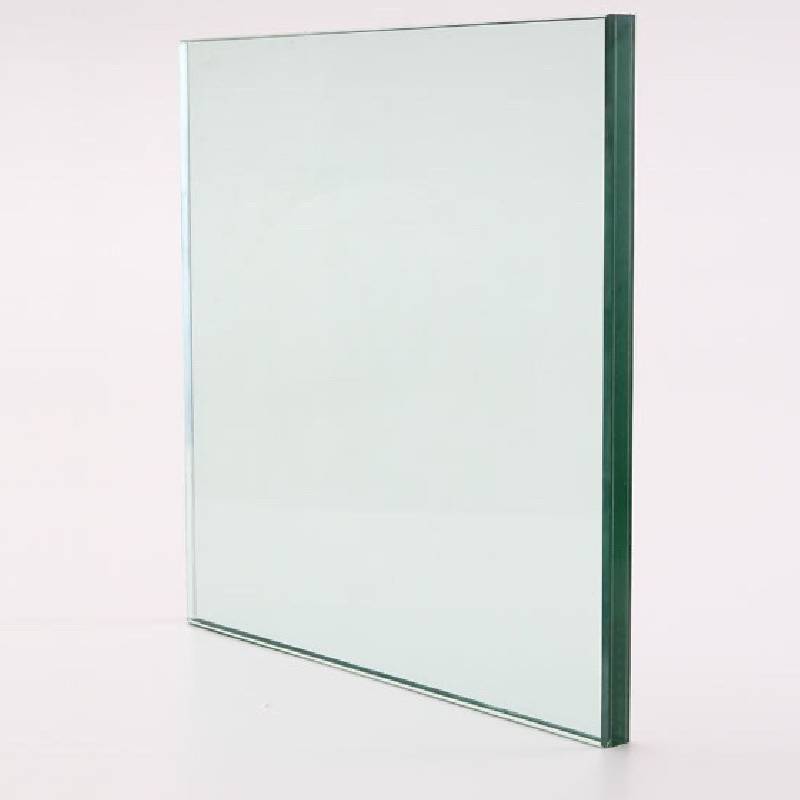
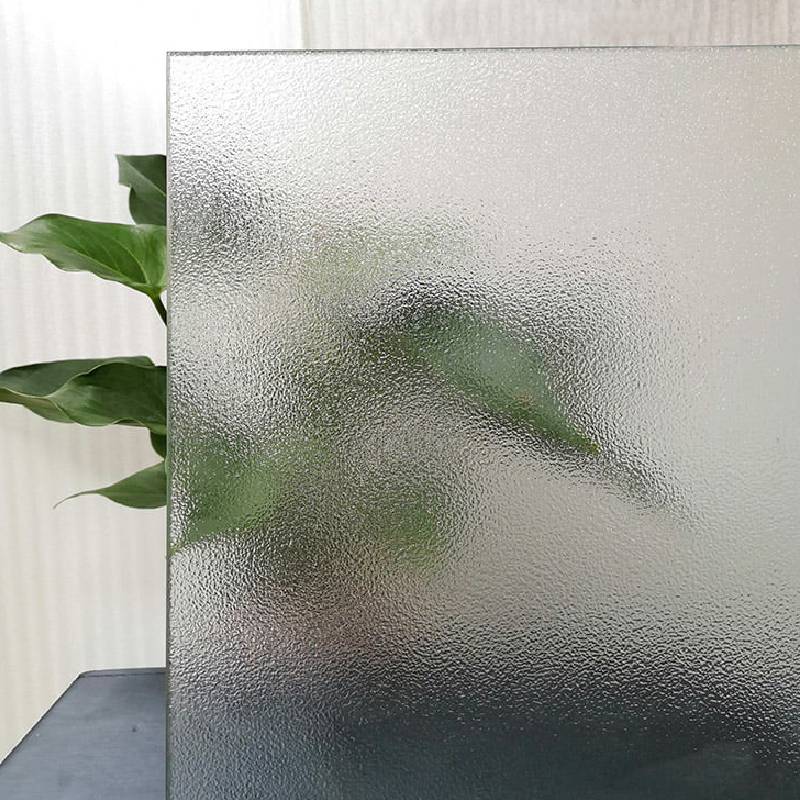
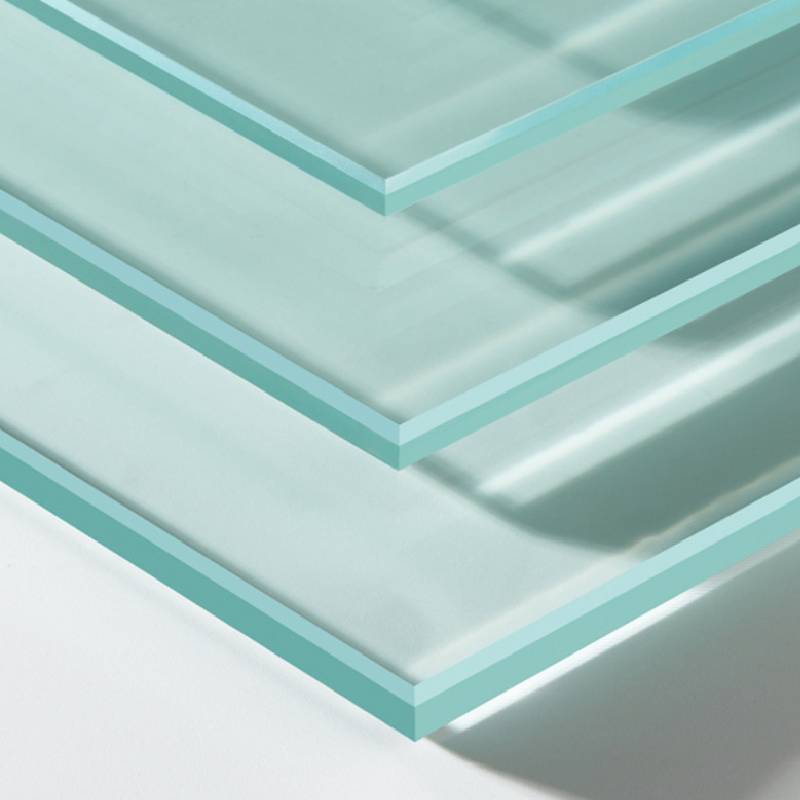
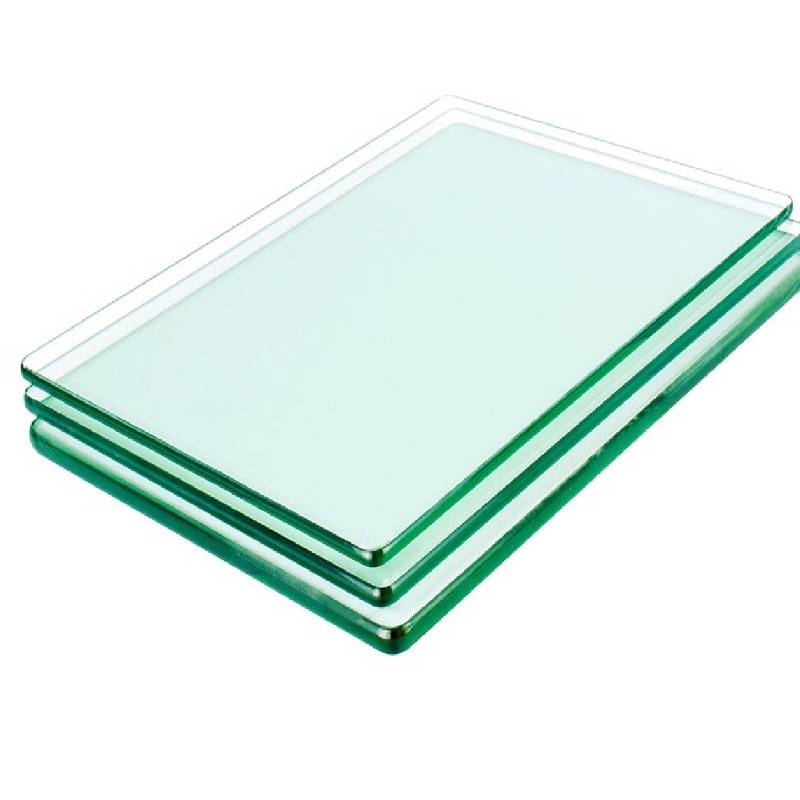
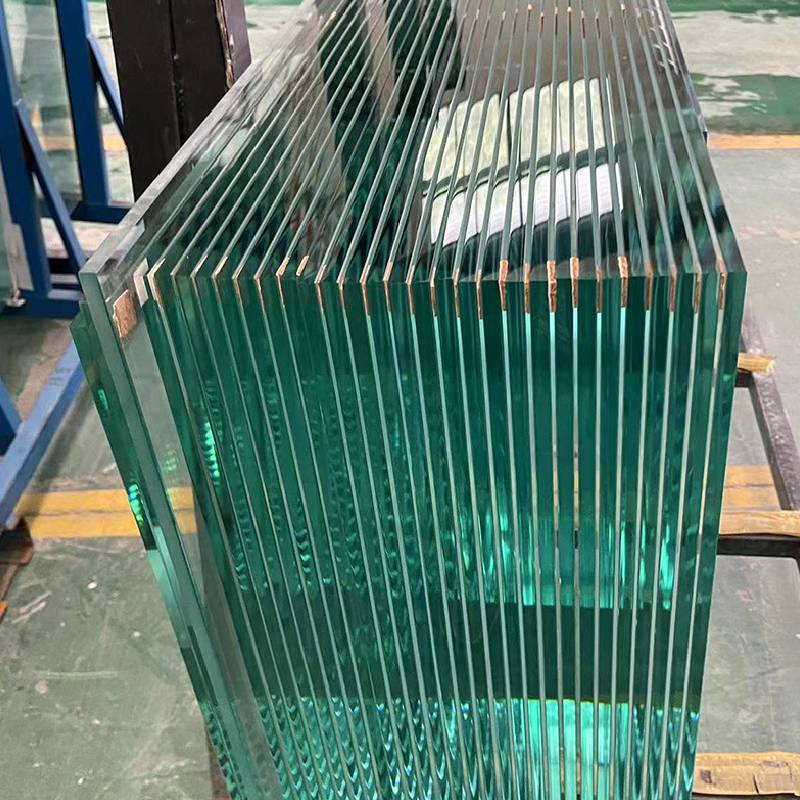
Tempered glass is made through a process called tempering, which involves heating annealed (regular) glass to a high temperature and then rapidly cooling it.
Cutting: The first step in the process is to cut the glass to the desired size and shape.
Cleaning: Once the glass is cut, it is thoroughly cleaned to remove any dirt, dust, or contaminants from the surface.
Heating: The cleaned glass is then placed into a tempering oven, which heats it to a temperature of around 620-680 degrees Celsius (1150-1250 degrees Fahrenheit).
Quenching: After the glass reaches the desired temperature, it is quickly cooled by blasting it with jets of cold air or by immersing it in a bath of cold water or oil.
Annealing: Once the glass is tempered, it undergoes a process called annealing to relieve the internal stress and strengthen the glass further. This involves heating the glass to a lower temperature and then slowly cooling it in a controlled manner. Annealing helps to ensure the stability and durability of the tempered glass.
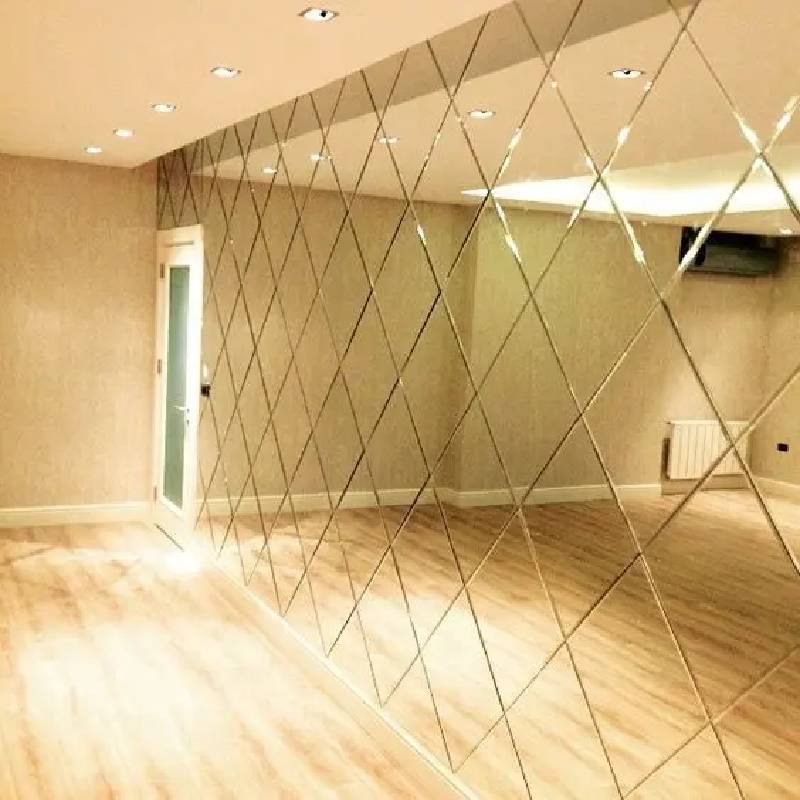
Strength: Tempered glass is significantly stronger than regular glass of the same thickness. It can withstand higher impact forces and is less likely to break upon impact. This makes it an ideal choice for applications where safety is a concern, such as in windows, doors , shower enclosures, and automotive windows.
Safety: When tempered glass does break, it shatters into small, blunt pieces rather than sharp shards. This reduces the risk of injury from sharp edges, making tempered glass safer for use in environments where breakage is a possibility.
Heat Resistance: Tempered glass has higher thermal resistance compared to regular glass. It can withstand sudden changes in temperature, such as exposure to hot or cold liquids, without shattering. This property makes it suitable for use in oven doors, cookware, and fireplace screens .
Manufacturing Process: Tempered glass is produced by heating annealed (regular) glass to a high temperature and then rapidly cooling it using air jets or quenching it in a bath of cold water or oil. This process creates internal stress within the glass, giving it its characteristic strength and safety features.
Tempered glass is used in a wide range of applications, including residential and commercial windows, glass doors, glass partitions, shower enclosures, tabletops, and automotive windows. Its strength and safety properties make it a popular choice in construction, automotive, and consumer electronics industries.
Overall, tempered glass offers enhanced strength, safety, and heat resistance compared to regular glass, making it a versatile and widely used material in various industries and applications.
The inspection standards for tempered glass mainly include the following aspects:
Fragmentation status: Different types of tempered glass have different requirements for their fragmentation status. For example, when the thickness of Class I tempered glass is 4mm, take 5 samples for testing, and the mass of the largest fragment among all 5 samples shall not exceed 15g. When the thickness is greater than or equal to 5mm, the number of fragments in each sample within the 50mm*50mm area must exceed 40.
Mechanical strength: The mechanical strength of tempered glass includes compression resistance, bending resistance and impact resistance. There are three inspection methods: tensile test, bending test and impact test.
Thermal stability: The thermal stability of tempered glass refers to its tolerance and deformation ability in high temperature environments. Inspection methods include differential thermal analysis, thermal expansion test, etc.
Size and deviation: The size of tempered glass is agreed upon by both the supplier and the buyer, and the allowable deviation of its side length should meet certain standards.
Appearance quality: The appearance quality of tempered glass must comply with certain regulations, including but not limited to hole diameter, hole position allowable deviation, etc.
Recommended national standards and industry standards for tempered glass testing include:
GB15763.2-2005 Safety glass for construction Part 2: Tempered glass: This standard specifies the basic requirements, test methods and inspection rules for safety glass for construction.
GB15763.4-2009 Safety glass for construction Part 4: Homogeneous tempered glass: This standard specifies the basic requirements, test methods and inspection rules for homogeneous tempered glass for construction.
JC/T1006-2018 Glazed tempered and glazed semi-tempered glass: This standard specifies the technical requirements, test methods and inspection rules for glazed tempered and glazed semi-tempered glass.
Thickness: 3.2mm, 4mm, 5mm, 6mm, 8mm, 10mm, 12mm
Size: customized according to customer requirements.
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans  Albanian
Albanian  Amharic
Amharic  Arabic
Arabic  Armenian
Armenian  Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani  Basque
Basque  Belarusian
Belarusian  Bengali
Bengali  Bosnian
Bosnian  Bulgarian
Bulgarian  Catalan
Catalan  Cebuano
Cebuano  Corsican
Corsican  Croatian
Croatian  Czech
Czech  Danish
Danish  Dutch
Dutch  English
English  Esperanto
Esperanto  Estonian
Estonian  Finnish
Finnish  French
French  Frisian
Frisian  Galician
Galician  Georgian
Georgian  German
German  Greek
Greek  Gujarati
Gujarati  Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole  hausa
hausa  hawaiian
hawaiian  Hebrew
Hebrew  Hindi
Hindi  Miao
Miao  Hungarian
Hungarian  Icelandic
Icelandic  igbo
igbo  Indonesian
Indonesian  irish
irish  Italian
Italian  Japanese
Japanese  Javanese
Javanese  Kannada
Kannada  kazakh
kazakh  Khmer
Khmer  Rwandese
Rwandese  Korean
Korean  Kurdish
Kurdish  Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz  Lao
Lao  Latin
Latin  Latvian
Latvian  Lithuanian
Lithuanian  Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish  Macedonian
Macedonian  Malgashi
Malgashi  Malay
Malay  Malayalam
Malayalam  Maltese
Maltese  Maori
Maori  Marathi
Marathi  Mongolian
Mongolian  Myanmar
Myanmar  Nepali
Nepali  Norwegian
Norwegian  Norwegian
Norwegian  Occitan
Occitan  Pashto
Pashto  Persian
Persian  Polish
Polish  Portuguese
Portuguese  Punjabi
Punjabi  Romanian
Romanian  Russian
Russian  Samoan
Samoan  Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic  Serbian
Serbian  Sesotho
Sesotho  Shona
Shona  Sindhi
Sindhi  Sinhala
Sinhala  Slovak
Slovak  Slovenian
Slovenian  Somali
Somali  Spanish
Spanish  Sundanese
Sundanese  Swahili
Swahili  Swedish
Swedish  Tagalog
Tagalog  Tajik
Tajik  Tamil
Tamil  Tatar
Tatar  Telugu
Telugu  Thai
Thai  Turkish
Turkish  Turkmen
Turkmen  Ukrainian
Ukrainian  Urdu
Urdu  Uighur
Uighur  Uzbek
Uzbek  Vietnamese
Vietnamese  Welsh
Welsh  Bantu
Bantu  Yiddish
Yiddish  Yoruba
Yoruba  Zulu
Zulu